Embarking on the journey of understanding What Causes Crohn's Disease and How to Treat It Effectively, this introduction aims to draw in readers with intriguing insights into the topic.
The subsequent paragraph will delve into providing a comprehensive overview of the subject matter.
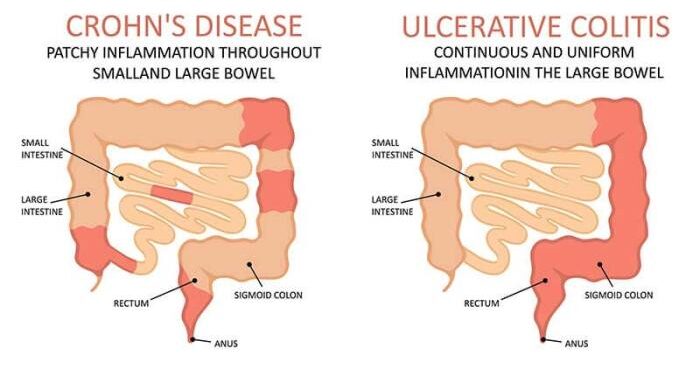
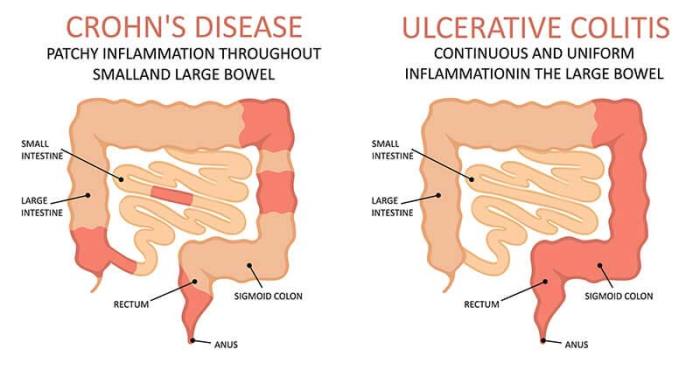
Understanding Crohn’s Disease
Crohn's disease is a chronic inflammatory condition that affects the digestive tract. It is classified as an inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) along with ulcerative colitis. The exact cause of Crohn's disease is unknown, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic, environmental, and immune system factors.
Symptoms of Crohn’s Disease
- Abdominal pain and cramping
- Diarrhea
- Weight loss
- Fatigue
- Bloody stools
Parts of the Digestive Tract Affected
Crohn's disease can affect any part of the digestive tract, from the mouth to the anus. However, it most commonly affects the end of the small intestine (ileum) and the beginning of the large intestine (colon).
Risk Factors for Crohn’s Disease
- Family history of Crohn's disease
- Smoking
- Age (usually diagnosed before age 30)
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) use
Causes of Crohn’s Disease
Crohn's disease is a complex condition with various factors that can contribute to its development. Understanding these causes is essential in managing the disease effectively.
Genetic Factors
Genetic predisposition plays a significant role in the development of Crohn's disease. Individuals with a family history of the condition are at a higher risk of developing it themselves. Specific gene mutations have been identified as potential triggers for Crohn's disease, highlighting the importance of genetic factors in its onset.
Immune System Dysfunction
The immune system also plays a crucial role in causing Crohn's disease. In individuals with the condition, the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy cells in the digestive tract, leading to inflammation and damage. This chronic immune response contributes to the symptoms experienced by Crohn's disease patients.
Environmental Triggers
Environmental factors can act as triggers for Crohn's disease in susceptible individuals. Factors such as smoking, diet, and exposure to certain pollutants have been linked to an increased risk of developing the condition. These external influences can exacerbate the immune response and inflammation in the digestive tract, worsening the symptoms of Crohn's disease.
Lifestyle Factors
Certain lifestyle choices can also influence the onset of Crohn's disease. Factors such as stress, lack of physical activity, and poor dietary habits can contribute to the development of the condition. Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including stress management techniques and a balanced diet, can help reduce the risk of developing Crohn's disease and improve overall well-being.
Diagnosing Crohn’s Disease
When it comes to Crohn's disease, the diagnostic process plays a crucial role in determining the appropriate treatment plan. Early detection is key to effectively managing the condition and improving the patient's quality of life. Let's explore the common tests used for diagnosing Crohn's disease and the importance of timely intervention.
Common Tests for Diagnosing Crohn’s Disease
- Colonoscopy: This procedure allows doctors to examine the entire colon and small intestine, enabling them to identify any inflammation, ulcers, or other signs of Crohn's disease.
- Endoscopy: By using a flexible tube with a camera, doctors can visualize the upper gastrointestinal tract to detect inflammation and other abnormalities associated with Crohn's disease.
- Imaging Tests (CT scan, MRI, or X-ray): These imaging techniques help in assessing the extent of inflammation and identifying complications such as strictures or fistulas in the digestive tract.
Importance of Early Detection in Managing Crohn’s Disease
Early diagnosis of Crohn's disease is crucial for initiating appropriate treatment and preventing complications. Timely intervention can help alleviate symptoms, reduce inflammation, and improve the overall prognosis for the patient. Regular monitoring and prompt adjustments to the treatment plan can enhance the patient's quality of life and prevent disease progression.
Differential Diagnoses for Crohn’s Disease
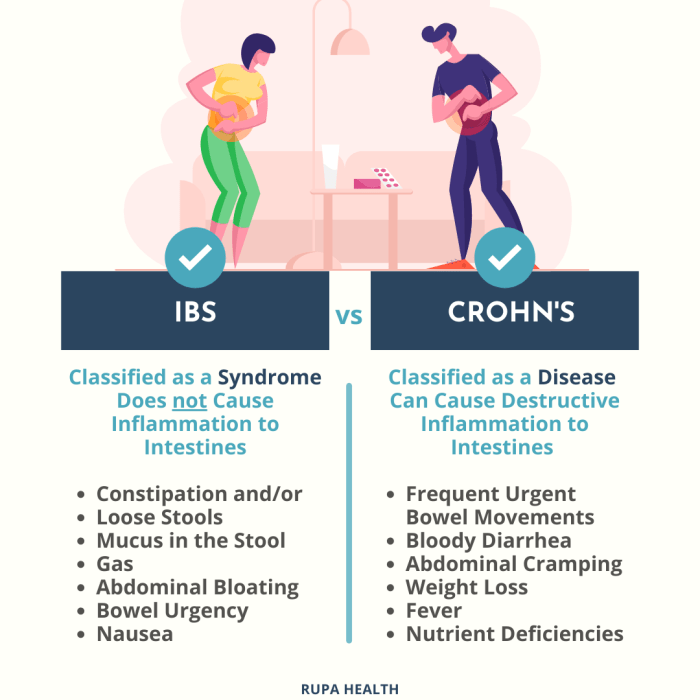
- Ulcerative Colitis: Another type of inflammatory bowel disease that shares similar symptoms with Crohn's disease but affects only the colon and rectum.
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS): A functional gastrointestinal disorder that can present with abdominal pain, bloating, and changes in bowel habits, often mistaken for Crohn's disease.
- Celiac Disease: An autoimmune disorder triggered by gluten consumption, which can cause gastrointestinal symptoms similar to those of Crohn's disease.
Treatment Options for Crohn’s Disease
Crohn's disease is a chronic condition that requires long-term management to control symptoms and prevent flare-ups. Treatment options for Crohn's disease typically involve a combination of medications, dietary changes, surgical interventions, and complementary therapies.
Medication Options for Managing Crohn’s Disease Symptoms
- Anti-inflammatory drugs: such as corticosteroids and aminosalicylates, help reduce inflammation in the digestive tract.
- Immunomodulators: like azathioprine and methotrexate, suppress the immune system's response to reduce inflammation.
- Biologics: such as infliximab and adalimumab, target specific proteins in the body to reduce inflammation.
- Antibiotics: can help treat bacterial overgrowth in the intestines that may worsen Crohn's symptoms.
Role of Diet and Nutrition in the Treatment of Crohn’s Disease
Diet plays a crucial role in managing Crohn's disease symptoms. A high-fiber diet may exacerbate symptoms, while low-residue diets can help reduce inflammation and discomfort. It's important to work with a healthcare provider or dietitian to create a personalized nutrition plan that meets your specific needs.
Surgical Interventions for Severe Cases of Crohn’s Disease
In severe cases of Crohn's disease where medications and lifestyle changes are not effective, surgery may be necessary. Surgical interventions can involve removing damaged portions of the intestines, repairing fistulas, or addressing complications such as strictures.
Examples of Complementary Therapies for Managing Crohn’s Disease
- Probiotics: may help restore a healthy balance of gut bacteria and reduce inflammation.
- Acupuncture: can help alleviate pain and reduce stress associated with Crohn's disease.
- Mind-body techniques: such as yoga and meditation, may help manage symptoms and improve overall well-being.
- Herbal supplements: some herbs like aloe vera and slippery elm may have anti-inflammatory properties that could benefit individuals with Crohn's disease.
Last Word
Concluding the discussion on What Causes Crohn's Disease and How to Treat It Effectively, this final section will offer a concise summary and closing remarks to wrap up the content.
FAQ Corner
What are common risk factors associated with Crohn's Disease?
Common risk factors include genetics, immune system dysfunction, environmental triggers, and lifestyle choices.
What role does diet play in managing Crohn's Disease?
Diet can significantly impact Crohn's Disease symptoms, with some foods triggering inflammation while others can help reduce flare-ups.
Are there any alternative therapies that can aid in managing Crohn's Disease?
Yes, complementary therapies like acupuncture, probiotics, and mind-body techniques have shown to be beneficial for some individuals with Crohn's Disease.